Minoan Civilization
Definition
Dolphin Fresco, Knossos, Crete
The Minoan civilization flourished in the Middle Bronze Age (c. 2000 - c. 1500 BCE) on the island of Crete located in the eastern Mediterranean. With their unique art and architecture, and the spread of their ideas through contact with other cultures across the Aegean, the Minoans made a significant contribution to the development of Western European civilization.
Labyrinth-like palace complexes, vivid frescoes depicting scenes such as bull-leaping and processions, fine gold jewellery, elegant stone vases, and pottery with vibrant decorations of marine life are all particular features of Minoan Crete.
Arthur Evans & Discovery
The archaeologist Sir Arthur Evans was first alerted to the possible presence of an ancient civilization on Crete by surviving carved seal stones worn as charms by native Cretans in the early 20th century CE. Excavating at Knossos from 1900 to 1905 CE, Evans discovered extensive ruins which confirmed the ancient accounts, both literary and mythological, of a sophisticated Cretan culture and possible site of the legendary labyrinth and palace of King Minos. It was Evans who coined the term Minoan in reference to this legendary Bronze Age king. Evans, seeing what he believed to be the growth and decline of a unified culture on Crete, divided the island's Bronze Age into three distinct phases largely based on different pottery styles:
- Early Bronze Age or Early Minoan (EM): 3000-2100 BCE
- Middle Bronze Age or Middle Minoan (MM): 2100-1600 BCE
- Late Bronze Age or Late Minoan (LM): 1600-1100 BCE
The above divisions were subsequently refined by adding numbered subphases to each group (e.g. MM II). Radio-carbon dating and tree-ring calibration techniques have helped to further refine the dates so that the Early Bronze Age now begins c. 3500 BCE and the Late Bronze Age c. 1700 BCE. An alternative to this series of divisions, created by Platon, instead focuses on the events occurring in and around the major Minoan “palaces”. This scheme has four periods:
- Prepalatial: 3000 - 2000/1900 BCE
- Protopalatial: 2000/1900 - 1700 BCE
- Neopalatial: 1700 - 1470/1450 BCE
- Postpalatial: 1470/1450 - 1100 BCE
Both of these schemes have since been challenged by more modern archaeology and approaches to history and anthropology in general which prefer a more multilinear development of culture on Crete with a more complex scenario involving conflicts and inequalities between settlements and which also considers their cultural differences as well as their obvious similarities.
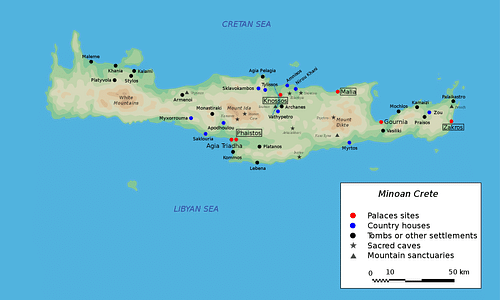
Minoan Palace Settlements
Minoan settlements, tombs, and cemeteries have been found all over Crete but the four principal palace sites (in order of size) were:
At each of these sites, large, complex palace structures seem to have acted as local administrative, trade, religious, and possibly political centres. The relationship between the palaces and the power structure within them or over the island as a whole is not clear due to a lack of archaeological and literary evidence. It is clear, however, that the palaces exerted some kind of localised control, in particular, in the gathering and storage of surplus materials - wine, oil, grain, precious metals and ceramics. Small towns, villages, and farms were spread around the territory seemingly controlled by a single palace. Roads connected these isolated settlements to each other and the main centre. There is a general agreement among historians that the palaces were independent from each other up to 1700 BCE, and thereafter they came under the sway of Knossos, as evidenced by a greater uniformity in architecture and the use of Linear A writing across various palace sites.
The absence of fortifications in the settlements suggests a relatively peaceful co-existence between the different communities. However, the presence of weapons such as swords, daggers, and arrowheads, and defensive equipment such as armour and helmets would also suggest that peace may not always have been enjoyed. Minoan roads, too, have evidence of regular guardhouses and watchtowers suggesting that banditry, at least, troubled the unprotected traveller.
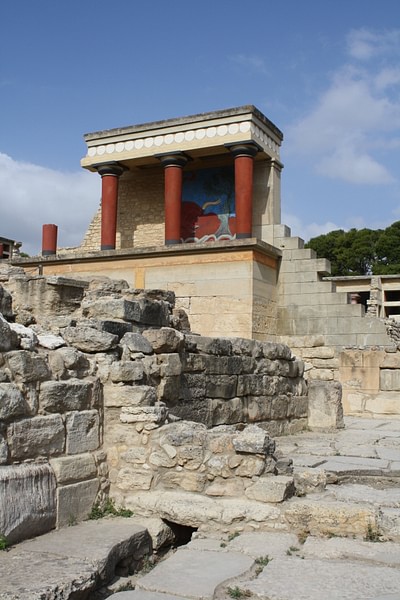

The palaces themselves covered two periods. The first palaces were constructed around 2000 BCE and, following destructive earthquakes and fires, rebuilt again c. 1700 BCE. These second palaces survived until their final destruction between 1500 BCE and 1450 BCE, once again by either earthquake, fire, or possibly invasion (or a combination of all three). The palaces were well-appointed, monumental structures with large courts, colonnades, ceilings supported by tapered wooden columns, staircases, religious crypts, light-wells, extensive drainage systems, large storage magazines and even 'theatre' areas for public spectacles or religious processions.
Reaching up to four stories high and spreading over several thousand square metres, the complexity of these palaces, the sport of bull-leaping, the worship of bulls as indicated by the presence throughout of sacred bulls' horns and depictions of double axes (or labrys) in stone and fresco may all have combined to give birth to the legend of Theseus and the labyrinth-dwelling Minotaur so popular in later classical Greek mythology.
Religion
The religion of the Minoans remains sketchy, but details are revealed through art, architecture, and artefacts. These include depictions of religious ceremonies and rituals such as the pouring of libations, making food offerings, processions, feasts, and sporting events like bull-leaping. Natural forces and nature in general, manifested in such artworks as a voluptuous female mother-earth goddess figure and male figure holding several animals, seem to have been revered. Palaces contain open courtyards for mass gatherings and rooms often have wells and channels for the pouring of libations, as previously noted. As already mentioned, too, bulls are prominent in Minoan art, and their horns are an architectural feature of palace walls and a general decorative element in jewellery, frescoes, and pottery decoration. Dramatic rural sites such as hilltops and caves often show evidence of cult rituals being performed there.

Material Culture
The sophistication of the Minoan culture and its trading capacity is evidenced by the presence of writing, firstly Cretan Hieroglyphic (c. 2000-1700 BCE) and then Linear A scripts (both, as yet, undeciphered), predominantly found on various types of administrative clay tablets. Seal impressions on clay were another important form of record keeping.
A further example of the culture's high degree of development is the variety and quality of the art forms practised by the Minoans. Pottery finds reveal a wide range of vessels from wafer-thin cups to large storage jars (pithoi). Ceramics were initially hand-turned but then increasingly made on the potter's wheel. In decoration, there was a progression from flowing geometric designs in Kamares ware to vibrant naturalistic depictions of flowers, plants, and sea life in the later Floral and Marine styles. Common pottery shapes include three-handled amphorae, tall beaked-jugs, squat round vessels with a false spout, beakers, small lidded boxes, and ritual vessels with figure-of-eight-shaped handles. Stone was also used to produce similar vessel types and rhyta (ritual vessels for pouring libations, often in the shape of animal heads).
Large-scale figure sculpture has not survived but there are many figurines in bronze and other materials. Early types in clay show the dress of the time with men (coloured red) wearing belted loincloths and women (coloured white) in long flowing dresses and open-fronted jackets. A leaping acrobat in ivory and the faience snake goddess already mentioned are notable works which reveal the Minoan love of capturing figures in active striking poses.

Magnificent frescoes from the walls, ceilings, and floors of the palaces also reveal the Minoans' love of the sea and nature and give insights into religious, communal, and funeral practices. Subjects range in scale from miniature to larger-than-life size. The Minoans were one of the earliest cultures to paint natural landscapes without any humans present in the scene; such was their admiration of nature. Animals, too, were often depicted in their natural habitat, for example, monkeys, birds, dolphins, and fish. Although Minoan frescoes were often framed with decorative borders of geometric designs, the principal fresco itself, on occasion, went beyond conventional boundaries such as corners and covered several walls of a single room, surrounding the viewer.
Aegean Contacts
The Minoans, as a seafaring culture, were also in contact with foreign peoples throughout the Aegean, as evidenced by the Near Eastern and Egyptian influences in their early art but also in the later export trade, notably the exchange of pottery and foodstuffs such as oil and wine in return for precious objects and materials such as copper from Cyprus and Attica and ivory from Egypt. Several Aegean islands, especially in the Cyclades, display the characteristics of a palace-centred economy and political structure as seen on Crete while Minoan artists, especially fresco painters, took their skills to the royal palaces of Egypt and the Levant.

Decline
The reasons for the demise of the Minoan civilization continue to be debated. Palaces and settlements show evidence of fire and destruction c. 1450 BCE, but not at Knossos (which was destroyed perhaps a century later). The rise of the Mycenaean civilization in the mid-2nd millennium BCE on the Greek mainland and the evidence of their cultural influence on later Minoan art and trade make them the most likely cause. However, other suggestions include earthquakes and volcanic activity with a consequent tsunami. The eruption of Thera (the present-day island of Santorini) may have been particularly significant, although, the exact date of this cataclysmic eruption is disputed and therefore its connection with the end of the Minoan period remains unclear. The most likely scenario was probably a fatal mix of natural environmental damage and competition for wealth weakening the structure of society, which was then exploited by invading Mycenaeans. Whatever the cause, most of the Minoan sites were abandoned by 1200 BCE and Crete would not return to the Mediterranean stage of history until the 8th century BCE when it was colonised by Archaic Greeks.
Map
Bibliography
- Bagnall, R.S. The Encyclopedia of Ancient History. Wiley-Blackwell, 2012
- Cline, E.H. The Oxford Handbook of the Bronze Age Aegean. Oxford University Press, USA, 2012.
- Davaras, C. East Crete. Hannibal, Athens
- Davaras, C. Malia. Hannibal, Athens
- Davaras, C. Phaistos. Hannibal, Athens
- Davaras, C. The Palace Of Knossos. Hannibal, Athens, 2010
- Higgins, R. Minoan and Mycenaean Art. Thames & Hudson, 1997.
- Hornblower, S. The Oxford Classical Dictionary. Oxford University Press, 2012.
- Hutchinson, R.W. Prehistoric Crete. Pelican / Penguin Books, 1963.
- Stylianos, A. Minoan Civilization. Heraclion, 1969.
- ====================================================================
 Definition
DefinitionMinoan Art
The art of the Minoan civilization of Bronze Age Crete (2000-1500 BCE) displays a love of animal, sea, and plant life, which was used to decorate frescoes and pottery and also inspired forms in jewellery, stone vessels... Definition
DefinitionMinoan Civilization
The Minoan civilization flourished in the Middle Bronze Age (c. 2000 - c. 1500 BCE) on the island of Crete located in the eastern Mediterranean. With their unique art and architecture, and the spread of their ideas through contact with other... Article
ArticleThe Minoans & Mycenaeans: Comparison of Two Bronze Age Civilisations
The Bronze Age Aegean in the eastern Mediterranean encompassed several powerful entities: the Minoans on Crete; the Mycenaeans on mainland Greece, and the Cypriots on Cyprus. These cultures are often examined separately, and thus the... Article
ArticleExploring Western Crete's Archaeological Treasures
As the cradle of European Civilization and a meeting place of diverse cultures, Crete is a magical island that stands apart in the heart of the Mediterranean sea. Its prominent place in world history dates back to the mysterious and fascinating... Article
ArticleMinoan Jewellery
The jewellery of the Minoan civilization based on Bronze Age Crete demonstrates, as with other Minoan visual art forms, not only a sophisticated technological knowledge (in this case of metalwork) and an ingenuity of design but also a joy... Article
ArticleMinoan Stoneware
Craftsmen of the Minoan civilization centred on the island of Crete produced stone vessels from the early Bronze Age (c. 2500 BCE) using a wide variety of stone types which were laboriously carved out to create vessels of all shapes, sizes... Article
ArticleMinoan Frescoes
Frescoes are the source of some of the most striking imagery handed down to us from the Minoan civilization of Bronze Age Crete (2000-1500 BCE). Further, without written records, they are often the only source, along with decorated pottery... Definition
DefinitionMinoan Architecture
The unique contribution of the Minoan civilization to European architecture is possibly most evident in the great palace structures of the major Minoan centres of Knossos, Phaistos, Malia and Zakros. Perhaps influenced by Egypt and the Near... Article
ArticleBeauty in the Bronze Age - Minoan & Mycenaean Fashion
Dress and appearance in Bronze Age Greece (c. 3100 BCE - c. 1100 BCE) played a part in defining gender roles and emphasising idealized beauty that planted the seed for modern-day standards. The Minoans turned the island of Crete into a Mediterranean... Article
ArticleMinoan Pottery
The ever evolving pottery from the Minoan civilization of Bronze Age Crete (2000-1500 BCE) demonstrates, perhaps better than any other medium, not only the Minoan joy in animal, sea and plant life but also their delight in flowing, naturalistic...Related Books on Amazon






